Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Clinical Study
- Relationship of Sarcopenia with Microcirculation Measured by Skin Perfusion Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Chan-Hee Jung, Yoon Young Cho, Dughyun Choi, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Ji-Oh Mok
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):578-586. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.679
- 5,371 View
- 122 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Few studies have examined the relationship of sarcopenia with the microcirculation. The current study investigated the relationship of sarcopenia with microcirculatory function, as assessed by skin perfusion pressure (SPP), in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
Methods
In total, 102 T2DM patients who underwent SPP measurements and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. SPP was assessed using the laser Doppler technique. Sarcopenia was defined as low height-adjusted appendicular muscle mass (men, <7 kg/m2; women, <5.7 kg/m2) using BIA. We divided the participants into two groups based on SPP (≤50 and >50 mm Hg), and an SPP below 50 mm Hg was considered to reflect impaired microcirculation.
Results
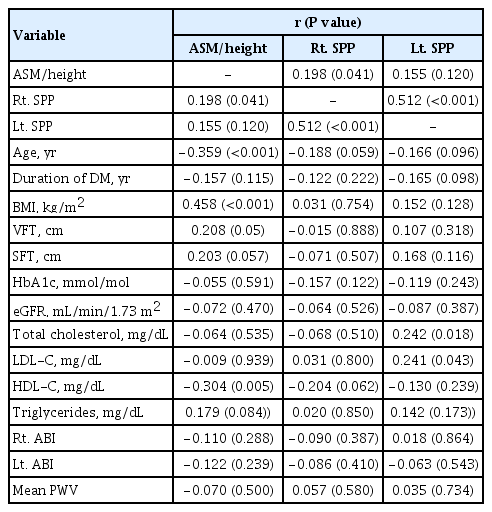
Fourteen patients (13.7%) were diagnosed with impaired microcirculatory function of the lower limb based on SPP. The prevalence of sarcopenia in all subjects was 11.8%, but the percentage of patients with an SPP ≤50 mm Hg who had sarcopenia was more than triple that of patients with an SPP >50 mm Hg (28.6% vs. 9.1%, P=0.036). A significant positive correlation was found between SPP and appendicular muscle mass adjusted for height (P=0.041 for right-sided SPP). Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that patients with sarcopenia had an odds ratio of 4.1 (95% confidence interval, 1.01 to 24.9) for having an SPP ≤50 mm Hg even after adjustment for confounding factors.
Conclusion
These results suggest that sarcopenia may be significantly associated with impaired microcirculation in patients with T2DM. Nonetheless, the small number of patients and wide CI require cautious interpretation of the results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preclinical study of diabetic foot ulcers: From pathogenesis to vivo/vitro models and clinical therapeutic transformation
Yuqing Du, Jie Wang, Weijing Fan, Renyan Huang, Hongfei Wang, Guobin Liu
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(10): 4394. CrossRef - Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for the Assessment of Body Composition in Sarcopenia and Type 2 Diabetes
Stefano Sbrignadello, Christian Göbl, Andrea Tura
Nutrients.2022; 14(9): 1864. CrossRef - Discrimination between possible sarcopenia and metabolic syndrome using the arterial pulse spectrum and machine-learning analysis
Li-Wei Wu, Te OuYoung, Yu-Chih Chiu, Ho-Feng Hsieh, Hsin Hsiu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yaqin Ai, Ruoxin Xu, Lingping Liu
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Preclinical study of diabetic foot ulcers: From pathogenesis to vivo/vitro models and clinical therapeutic transformation

- Diabetes
- Recent Updates on Vascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):260-271. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.260
- 7,605 View
- 282 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
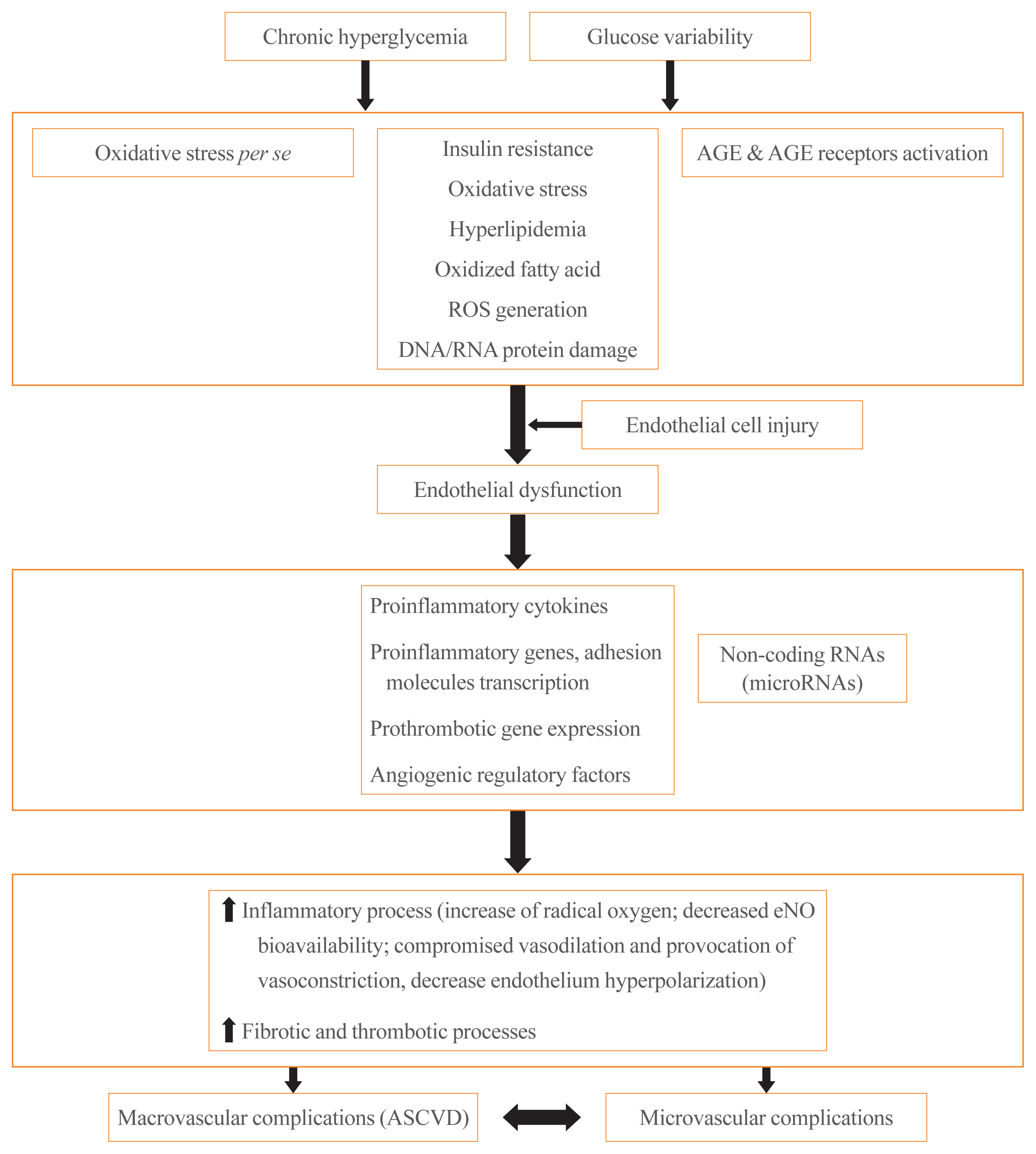
ePub - It is well known that patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are at an increased risk of morbidity and mortality from atherosclerotic cardiovascular (CV) complications. Previously, the concept that diabetes mellitus (DM) is a “coronary artery disease (CAD) risk equivalent” was widely accepted, implying that all DM patients should receive intensive management. However, considerable evidence exist for wide heterogeneity in the risk of CV events among T2DM patients and the concept of a “CAD risk equivalent” has changed. Recent guidelines recommend further CV risk stratification in T2DM patients, with treatment tailored to the risk level. Although imaging modalities for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been used to improve risk prediction, there is currently no evidence that imaging-oriented therapy improves clinical outcomes. Therefore, controversy remains whether we should screen for CVD in asymptomatic T2DM. The coexistence of T2DM and heart failure (HF) is common. Based on recent CV outcome trials, sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists are recommended who have established ASCVD, indicators of high risk, or HF because of their demonstrated benefits for CVD. These circumstances have led to an increasing emphasis on ASCVD and HF in T2DM patients. In this review, we examine the literature published within the last 5 years on the risk assessment of CVD in asymptomatic T2DM patients. In particular, we review recent guidelines regarding screening for CVD and research focusing on the role of coronary artery calcium, coronary computed tomography angiography, and carotid intima-media thickness in asymptomatic T2DM patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Orsolya-Zsuzsa Akácsos-Szász, Sándor Pál, Kinga-Ilona Nyulas, Enikő Nemes-Nagy, Ana-Maria Fárr, Lóránd Dénes, Mónika Szilveszter, Erika-Gyöngyi Bán, Mariana Cornelia Tilinca, Zsuzsánna Simon-Szabó
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4319. CrossRef - Increased soluble endoglin levels in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients are associated with endothelial dysfunction
Xiaobing Dou, Xiujing Wang, Xiuhua Yu, Jiaqi Yao, Huiling Shen, Yao Xu, Bojing Zheng, Zhenying Zhang, Qingying Tan, Tianxiao Hu
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(7): 711. CrossRef - Effects of hypertension on subcortical nucleus morphological alternations in patients with type 2 diabetes
Feng Cui, Zhi-Qiang Ouyang, Yi-Zhen Zeng, Bing-Bing Ling, Li Shi, Yun Zhu, He-Yi Gu, Wan-Lin Jiang, Ting Zhou, Xue-Jin Sun, Dan Han, Yi Lu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 568. CrossRef - Exploring Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells to Better Understand the Pathophysiology of Disease: An Updated Review
Qiuwang Zhang, Anthony Cannavicci, Michael J. B. Kutryk, Giuseppe Mandraffino
Stem Cells International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Recent Insights into the Nutritional Antioxidant Therapy in Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Vascular Complications: A Comprehensive Review
Narasimha M. Beeraka, Irina K. Tomilova, Galina A. Batrak, Maria V. Zhaburina, Vladimir N. Nikolenko, Mikhail Y. Sinelnikov, Liudmila M. Mikhaleva
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 29(11): 1920. CrossRef - Topical Reappraisal of Molecular Pharmacological Approaches to Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus Angiopathy
Constantin Munteanu, Mariana Rotariu, Marius-Alexandru Turnea, Aurelian Anghelescu, Irina Albadi, Gabriela Dogaru, Sînziana Calina Silișteanu, Elena Valentina Ionescu, Florentina Carmen Firan, Anca Mirela Ionescu, Carmen Oprea, Gelu Onose
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2022; 44(8): 3378. CrossRef - Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
Fei Xu, Xiang Ning, Tong Zhao, Qinghua Lu, Huiqiang Chen
Open Medicine.2022; 17(1): 1405. CrossRef - Effects of dulaglutide on endothelial progenitor cells and arterial elasticity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dandan Xie, Yutong Li, Murong Xu, Xiaotong Zhao, Mingwei Chen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum netrin and VCAM-1 as biomarker for Egyptian patients with type IΙ diabetes mellitus
Maher M. Fadel, Faten R. Abdel Ghaffar, Shimaa K. Zwain, Hany M. Ibrahim, Eman AE. badr
Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports.2021; 27: 101045. CrossRef - Decoding the chemical composition and pharmacological mechanisms of Jiedu Tongluo Tiaogan Formula using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with network pharmacology-based investigation
Qi Zhang, Chunli Piao, Wenqi Jin, De Jin, Han Wang, Cheng Tang, Xiaohua Zhao, Naiwen Zhang, Shengnan Gao, Fengmei Lian
Aging.2021; 13(21): 24290. CrossRef
- Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients

- Clinical Study
- Effect of Dapagliflozin on Alanine Aminotransferase Improvement in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Dug-Hyun Choi, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Bo-Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):387-394. Published online September 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.387
- 5,280 View
- 106 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) are expected to improve the liver function of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) combined type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by its characteristic mechanism. This study was designed to investigate the effect of dapagliflozin, one of the SGLT2i, on the liver function of T2DM with NAFLD when combined with metformin.
Methods Among patients who received dual oral hypoglycemic agents within the 3 months of diagnosing NAFLD, patients who had abnormal alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level (>40 IU/L) were included. Patients were divided into two groups: metformin+dapagliflozin group and metformin+dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i) group. Demographic data, biochemical data and the clinical and treatment histories of all patients were reviewed.
Results A total of 102 patients were included (dapagliflozin group,
n =50; DPP4i group,n =52). Dapagliflozin group showed more weight loss and more ALT decline than DPP4i group (−2.9 kg vs. −0.4 kg,P =0.005; −21.1 U/L vs. −9.5 U/L,P =0.008, respectively) and the proportion of patients with ALT normalization after treatment was also significantly higher in the dapagliflozin group (80.0% vs. 61.5%,P =0.041). The effect of dapagliflozin with metformin on ALT normalization remained significant after adjustment for confounding variables including body weight loss (odds ratio, 3.489;P =0.046).Conclusion ALT improvement was statistically significant in the dapagliflozin than the DPP4i when combined with metformin and the result was consistent after adjustment for confounding variables including body weight loss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of anti-diabetic drugs in NAFLD. Have we found the Holy Grail? A narrative review
Maria Zachou, Pagona Flevari, Narjes Nasiri-Ansari, Constantinos Varytimiadis, Evangelos Kalaitzakis, Eva Kassi, Theodoros Androutsakos
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2024; 80(1): 127. CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors on liver function in patients with type 2 diabetes in Japan: A real‐world data analysis
Hirokazu Takahashi, Keiko Asakawa, Yoshinori Kosakai, Takumi Lee, Mitsuhiro Rokuda
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 997. CrossRef - Effects of a Combination of Empagliflozin Plus Metformin vs. Metformin Monotherapy on NAFLD Progression in Type 2 Diabetes: The IMAGIN Pilot Study
Alfredo Caturano, Raffaele Galiero, Giuseppe Loffredo, Erica Vetrano, Giulia Medicamento, Carlo Acierno, Luca Rinaldi, Aldo Marrone, Teresa Salvatore, Marcellino Monda, Celestino Sardu, Raffaele Marfella, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 322. CrossRef - Swimming exercise ameliorates insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver by negatively regulating PPARγ transcriptional network in mice fed high fat diet
Yong Zhang, Jie Xu, Di Zhou, Tingting Ye, Puqing Zhou, Zuofeng Liu, Xinyuan Liu, Zinan Wang, Tianmiao Hua, Zhenghao Zhang, Qingyan Sun
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Heart Failure in Adults—A Systematic Review
Agnieszka Polecka, Natalia Olszewska, Łukasz Danielski, Ewa Olszewska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(19): 6139. CrossRef - Prospects of using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
Iryna Kostitska, Nadia Protas, Liliia Petrovska
Diabetes Obesity Metabolic Syndrome.2023; (5): 8. CrossRef - Therapeutic outcome of dapagliflozin on various parameters in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients
Mazhar Hussain, Muhammad Zafar Majeed Babar, Saba Tariq, Muhammad Irfan Ahmad, Lubna Akhtar
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(2): 290. CrossRef - The safety and efficacy evaluation of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors for patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An updated meta-analysis
Manqiu Mo, Zichun Huang, Yuzhen Liang, Yunhua Liao, Ning Xia
Digestive and Liver Disease.2022; 54(4): 461. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin improves steatohepatitis in diabetic rats via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
Reem M. Hazem, Ahmed Z. Ibrahim, Dina A. Ali, Yasser M. Moustafa
International Immunopharmacology.2022; 104: 108503. CrossRef - SGLT-2 Inhibitors in NAFLD: Expanding Their Role beyond Diabetes and Cardioprotection
Theodoros Androutsakos, Narjes Nasiri-Ansari, Athanasios-Dimitrios Bakasis, Ioannis Kyrou, Efstathios Efstathopoulos, Harpal S. Randeva, Eva Kassi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(6): 3107. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin protects against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in db/db mice
Panshuang Qiao, Yingli Jia, Ang Ma, Jinzhao He, Chen Shao, Xiaowei Li, Shuyuan Wang, Baoxue Yang, Hong Zhou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Tofogliflozin and Glimepiride Effects on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Participants With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, 48-Week, Open-Label, Active-Controlled Trial
Yumie Takeshita, Masao Honda, Kenichi Harada, Yuki Kita, Noboru Takata, Hiromasa Tsujiguchi, Takeo Tanaka, Hisanori Goto, Yujiro Nakano, Noriho Iida, Kuniaki Arai, Tatsuya Yamashita, Eishiro Mizukoshi, Hiroyuki Nakamura, Shuichi Kaneko, Toshinari Takamura
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(9): 2064. CrossRef - Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Novel Paradigm for Additional Cardiovascular Benefit of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Subjects With or Without Type 2 Diabetes
Vincenzo Maria Monda, Sandro Gentile, Francesca Porcellati, Ersilia Satta, Alessandro Fucili, Marcello Monesi, Felice Strollo
Advances in Therapy.2022; 39(11): 4837. CrossRef - Metformin, pioglitazone, dapagliflozin and their combinations ameliorate manifestations associated with NAFLD in rats via anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms
Hager H. Shaaban, Ibrahim Alzaim, Ahmed El-Mallah, Rania G. Aly, Ahmed F. El-Yazbi, Ahmed Wahid
Life Sciences.2022; 308: 120956. CrossRef - The impact of sodium glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitors on non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Lampros Chrysavgis, Alkistis‐Maria Papatheodoridi, Antonios Chatzigeorgiou, Evangelos Cholongitas
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(4): 893. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Asian Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Chloe Wong, Clyve Yu Leon Yaow, Cheng Han Ng, Yip Han Chin, Yi Fen Low, Amanda Yuan Ling Lim, Mark Dhinesh Muthiah, Chin Meng Khoo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitors on liver parameters and steatosis: A meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials
Francisca dos Santos Coelho, Marta Borges‐Canha, Madalena von Hafe, João Sérgio Neves, Catarina Vale, Ana Rita Leite, Davide Carvalho, Adelino Leite‐Moreira
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of anti-diabetic treatments in type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease
Elizabeth M. Lamos, Megan Kristan, Maka Siamashvili, Stephen N. Davis
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2021; 14(7): 837. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Ameliorate Liver Enzyme Abnormalities in Korean Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Won Euh, Soo Lim, Jin-Wook Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Dapagliflozin attenuates steatosis in livers of high-fat diet-induced mice and oleic acid-treated L02 cells via regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway
Jingyi Luo, Pengbo Sun, Yangyang Wang, Yang Chen, Yaoyun Niu, Yipei Ding, Naihan Xu, Yaou Zhang, Weidong Xie
European Journal of Pharmacology.2021; 907: 174304. CrossRef - The effects of dapagliflozin on hepatic and visceral fat in type 2 diabetes patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Susrichit Phrueksotsai, Kanokwan Pinyopornpanish, Juntima Euathrongchit, Apinya Leerapun, Arintaya Phrommintikul, Supawan Buranapin, Nipon Chattipakorn, Satawat Thongsawat
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(10): 2952. CrossRef - Possible Preventative/Rehabilitative Role of Gliflozins in OSA and T2DM. A Systematic Literature Review-Based Hypothesis
Vincenzo Maria Monda, Francesca Porcellati, Felice Strollo, Alessandro Fucili, Marcello Monesi, Ersilia Satta, Sandro Gentile
Advances in Therapy.2021; 38(8): 4195. CrossRef - Sodium‐glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitors reduce hepatic events in diabetic patients with chronic hepatitis B
Lilian Yan Liang, Vincent Wai‐Sun Wong, Vicki Wing‐Ki Hui, Terry Cheuk‐Fung Yip, Yee‐Kit Tse, Grace Chung‐Yan Lui, Henry Lik‐Yuen Chan, Grace Lai‐Hung Wong
GastroHep.2021; 3(4): 261. CrossRef - Effects of Metformin on Hepatic Steatosis in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: Insights from the Cellular to Patient Levels
Kanokwan Pinyopornpanish, Apinya Leerapun, Kanokporn Pinyopornpanish, Nipon Chattipakorn
Gut and Liver.2021; 15(6): 827. CrossRef - The Race to Bash NASH: Emerging Targets and Drug Development in a Complex Liver Disease
F. Anthony Romero, Christopher T. Jones, Yingzi Xu, Martijn Fenaux, Randall L. Halcomb
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2020; 63(10): 5031. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors in Liver Patients
John Chen Hsiang, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2020; 18(10): 2168. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef - Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics
Stergios A. Polyzos, Jannis Kountouras, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 92: 82. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: Part II: Treatment
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Yong Jin Kim, Dae Ho Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(2): 127. CrossRef - Concurrent exercise improves insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by upregulating PPAR-γ and genes involved in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids in ApoE-KO mice fed a high-fat diet
Fan Zheng, Ying Cai
Lipids in Health and Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Hypoglycemic Agents on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Focused on Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(1): 18. CrossRef - Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Ex quo et quo vadimus?
Niki Katsiki, Nikolaos Perakakis, Christos Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 98: iii. CrossRef - Empaglifozin mitigates NAFLD in high-fat-fed mice by alleviating insulin resistance, lipogenesis and ER stress
Tamiris Ingrid Petito-da-Silva, Vanessa Souza-Mello, Sandra Barbosa-da-Silva
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2019; 498: 110539. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on fatty liver in type 2 diabetes: A common comorbidity associated with severe complications
A.J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2019; 45(3): 213. CrossRef
- The role of anti-diabetic drugs in NAFLD. Have we found the Holy Grail? A narrative review

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Serum Concentrations of Ghrelin and Leptin according to Thyroid Hormone Condition, and Their Correlations with Insulin Resistance
- Kyu-Jin Kim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Chan-Hee Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):318-325. Published online May 18, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.318
- 3,856 View
- 45 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Thyroid hormones can influence energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity via their interaction with adipocytokines and gut hormones. The aims of this study were to evaluate differences in serum ghrelin and leptin concentrations according to thyroid hormone levels, and to investigate the correlation of insulin resistance.
Methods A total of 154 patients (57 hyperthyroid patients, 61 euthyroid patients, and 36 hypothyroid patients; mean age, 47.9 years) were enrolled. Serum leptin, ghrelin, and insulin levels were measured and insulin resistance was calculated using the formula of the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR).
Results There were no differences in mean concentrations of ghrelin or leptin among the three groups. There were no significant differences in insulin levels between the groups (
P =0.06), although hyperthyroid patients had borderline statistically significantly higher levels of insulin than did euthyroid subjects bypost hoc test (26.4 µIU/mL vs. 16.1 µIU/mL,P =0.057). Regarding HOMA-IR index, the mean levels were highest in the hyperthyroid group among those of the three groups (hyperthyroid vs. euthyroid vs. hypothyroid, 6.7 vs. 3.8 vs. 4.4,P =0.068). Plasma levels of ghrelin were significantly negatively correlated with age, insulin, glucose, body mass index (BMI), and HOMA-IR. Plasma levels of leptin showed significant positive correlation with BMI and triglyceride. There were no significant correlations among thyroid hormone, thyrotropin, ghrelin, leptin, or insulin.Conclusion The present study found that serum ghrelin, leptin, and insulin levels didn't differ according to thyroid function conditions. Further studies with larger numbers of patients are required to establish a direct relationship between plasma ghrelin, leptin, and thyroid hormone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin resistance, leptin and adiponectin in lean and hypothyroid children and adolescents with obesity
Doaa El Amrousy, Dalia El-Afify, Shaimaa Salah
BMC Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediators of energy homeostasis in hyperthyroidism
Avinash Patil, Suresh Vaikkakara, Mani Deepthi Dasari, Sandeep Ganta, Alok Sachan, Kiranmayi S. Vinapamula
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - STUDY OF GHRELIN LEVELS IN HYPOTHYROID PATIENTS BEFORE AND AFTER
TREATMENT
Peeyush Yadav, G. G. Kaushik
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 52. CrossRef - Acylated Ghrelin Attenuates l-Thyroxin–induced Cardiac Damage in Rats by Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects and Downregulating Components of the Cardiac Renin–angiotensin System
Rehab Badi
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2021; 78(3): 422. CrossRef - Experimental hypothyroidism in adult male rats: the effects of Artemisia dracunculus aqueous extract on serum thyroid hormones, lipid profile, leptin, adiponectin, and antioxidant factors
Mohammad Mohsen Mohammadi, Mahdi Saeb, Saeed Nazifi
Comparative Clinical Pathology.2020; 29(2): 485. CrossRef - Leptin, neuropeptide Y (NPY), melatonin and zinc levels in experimental hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism: relation with melatonin and the pineal gland
Abdulkerim Kasım Baltaci, Rasim Mogulkoc
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Leptin, NPY, Melatonin and Zinc Levels in Experimental Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism: The Relation to Zinc
Abdulkerim Kasım Baltaci, Rasim Mogulkoc
Biochemical Genetics.2017; 55(3): 223. CrossRef - Thyroid Hormone Regulation and Insulin Resistance: Insights From Animals Naturally Adapted to Fasting
Bridget Martinez, Rudy M. Ortiz
Physiology.2017; 32(2): 141. CrossRef - Role of the Orexin System on the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis
Antonietta Messina, Carolina De Fusco, Vincenzo Monda, Maria Esposito, Fiorenzo Moscatelli, Anna Valenzano, Marco Carotenuto, Emanuela Viggiano, Sergio Chieffi, Vincenzo De Luca, Giuseppe Cibelli, Marcellino Monda, Giovanni Messina
Frontiers in Neural Circuits.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Concentrations of Ghrelin and Leptin according to Thyroid Hormone Condition, and Their Correlations with Insulin Resistance (Endocrinol Metab2015;30:318-25, Kyu-Jin Kim et al.)
Jin Hwa Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 631. CrossRef - Serum Concentrations of Ghrelin and Leptin according to Thyroid Hormone Condition, and Their Correlations with Insulin Resistance (Endocrinol Metab2015;30:318-25, Kyu-Jin Kim et al.)
Chan-Hee Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 633. CrossRef
- Insulin resistance, leptin and adiponectin in lean and hypothyroid children and adolescents with obesity

- Adrenal gland
- Clinical Characteristics and Metabolic Features of Patients with Adrenal Incidentalomas with or without Subclinical Cushing's Syndrome
- Bo-Yeon Kim, A-Reum Chun, Kyu-Jin Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Sung Koo Kang, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):457-463. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.457
- 4,139 View
- 45 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to examine the clinical characteristics of adrenal incidentalomas discovered by computed tomography (CT) and to investigate metabolic features of subclinical Cushing's syndrome (SCS) in patients with adrenal incidentalomas in a tertiary hospital in Korea.
Methods This retrospective study examined the clinical aspects of 268 patients with adrenal incidentalomas discovered by CT at Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital. Clinical data and endocrine function of the patients as well as histological findings were obtained from medical records, while anatomic characteristics were analyzed by reviewing imaging studies. Hormonal tests for pheochromocytoma, Cushing's syndrome, and aldosterone-secreting adenoma were performed.
Results Most (
n =218, 81.3%) cases were nonfunctioning tumors. Of the 50 patients with functioning tumors (18.7%), 19 (7.1%) were diagnosed with SCS, nine (3.4%) with overt Cushing's syndrome, 12 (4.5%) with primary aldosteronism, and 10 (3.7%) with pheochromocytoma. Malignant tumors (both primary and metastatic) were rare (n =2, 0.7%). Body mass index, fasting glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and total cholesterol were significantly higher in patients with SCS in comparison with those with nonfunctioning tumors. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension were significantly higher in patients with SCS compared with those with nonfunctioning tumors.Conclusion Functioning tumors, especially those with subclinical cortisol excess, are commonly found in patients with adrenal incidentalomas, although malignancy is rare. In addition, patients with SCS in adrenal incidentalomas have adverse metabolic and cardiovascular profiles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of Adrenal Cortical Adenomas: Assessment of Bone Status in Patients with (Non-Functioning) Adrenal Incidentalomas
Alexandra-Ioana Trandafir, Mihaela Stanciu, Simona Elena Albu, Vasile Razvan Stoian, Irina Ciofu, Cristian Persu, Claudiu Nistor, Mara Carsote
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4244. CrossRef - Adrenalectomy improves blood pressure control in nonfunctioning adrenal incidentalomas and glycemic and lipid control in patients with autonomous cortisol secretion
Marta Araujo-Castro, César Mínguez Ojeda, María Noelia Sánchez Ramírez, Victoria Gómez Dos Santos, Eider Pascual-Corrrales, María Fernández-Argüeso
Endocrine.2022; 78(1): 142. CrossRef - Depression was associated with younger age, female sex, obesity, smoking, and physical inactivity, in 1027 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a Swedish multicentre cross-sectional study
Eva O. Melin, Pär Wanby, Thomas Neumark, Sara Holmberg, Ann-Sofi Nilsson Neumark, Karin Johansson, Mona Landin-Olsson, Hans Thulesius, Magnus Hillman, Maria Thunander
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and Visceral Adiposity Index in non-functional adrenal adenomas
Savas Karatas, Yalcin Hacioglu, Selvihan Beysel
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - DHEAS and Differential Blood Counts as Indirect Signs of
Glucocorticoid Excess in Adrenal Non-Producing Adenomas
Eliza P. Winzinger, Hana Jandikova, Matthias Haase, Andreas Knauerhase, Tudor Winzinger, Matthias Schott, Holger S. Willenberg
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2021; 53(08): 512. CrossRef - Links between aldosterone excess and metabolic complications: A comprehensive review
C. Bothou, F. Beuschlein, A. Spyroglou
Diabetes & Metabolism.2020; 46(1): 1. CrossRef - Presentation and outcome of patients with an adrenal mass: A retrospective observational study
Nadeema Rafiq, Tauseef Nabi, SajadAhmad Dar, Shahnawaz Rasool
Clinical Cancer Investigation Journal.2020; 9(5): 198. CrossRef - Malignancy Risk and Hormonal Activity of Adrenal Incidentalomas in a Large Cohort of Patients from a Single Tertiary Reference Center
Ewa Cyranska-Chyrek, Ewelina Szczepanek-Parulska, Michal Olejarz, Marek Ruchala
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(10): 1872. CrossRef - Biochemical and clinical characteristics of patients with primary aldosteronism – single centre experience
Nataša Vujačić, Ivan Paunović, Aleksandar Diklić, Vladan Živaljević, Nikola Slijepčević, Nevena Kalezić, Mirjana Stojković, Miloš Stojanović, Biljana Beleslin, Miloš Žarković, Jasmina Ćirić
Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The association of low muscle mass with soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE): The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS)
Tae Nyun Kim, Man Sik Park, Eun Joo Lee, Hye Soo Chung, Hye Jin Yoo, Hyun Joo Kang, Wook Song, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonfunctioning adrenal incidentaloma: A novel predictive factor for metabolic syndrome
Emanuela M. Ribeiro Cavalari, Marcela P. de Paula, Mariana Arruda, Nathália Carraro, Arthur Martins, Kamila de Souza, Maria C. Coelho, Nathalie Anne de Oliveira e Silva de Morais, Aline B. Moraes, Leonardo Vieira Neto
Clinical Endocrinology.2018; 89(5): 586. CrossRef - Guidelines for the Management of Adrenal Incidentaloma: the Korean Endocrine Society, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines
Jung-Min Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jung-Min Koh, Bo-Yeon Kim, Sang-Wan Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hae-Jin Kim, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Juri Park, Jung-Soo Lim, Seong Yeon Kim, Young Kee Shong, Soon Jib Yoo
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2017; 92(1): 4. CrossRef - Glucose Metabolism Abnormalities in Cushing Syndrome: From Molecular Basis to Clinical Management
Carla Scaroni, Marialuisa Zilio, Michelangelo Foti, Marco Boscaro
Endocrine Reviews.2017; 38(3): 189. CrossRef - Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Adrenal Incidentaloma
Jung-Min Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jung-Min Koh, Bo-Yeon Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Juri Park, Jung Soo Lim, Seong Yeon Kim, Young Kee Shong, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 200. CrossRef - Increased 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 and 17α-hydroxylase activities in a virilized adolescent female with adrenal adenoma: A case report
GUOQING YANG, JINGTAO DOU, XIAOLIN ZHANG, WEIJUN GU, ZHAOHUI LV, JIN DU, JIANMING BA, YIMING MU, JUMING LU
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2016; 11(2): 530. CrossRef - Subclinical hypercortisolism: a state, a syndrome, or a disease?
Guido Di Dalmazi, Renato Pasquali, Felix Beuschlein, Martin Reincke
European Journal of Endocrinology.2015; 173(4): M61. CrossRef - Metabolic comorbidities in Cushing's syndrome
Francesco Ferraù, Márta Korbonits
European Journal of Endocrinology.2015; 173(4): M133. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Incidentally Discovered Aldosterone and Cortisol Cosecreting Adrenal Cortical Adenoma
Ji Yun Bae, Jihyun Lee, Yeji Han, Seog Ki Min, Min-Sun Cho, Yeon-Ah Sung
The Ewha Medical Journal.2015; 38(3): 129. CrossRef - Subclinical Cushing's Syndrome and Metabolic Disorder
Ji Cheol Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(4): 441. CrossRef
- Management of Adrenal Cortical Adenomas: Assessment of Bone Status in Patients with (Non-Functioning) Adrenal Incidentalomas

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Response: Association between Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy, Diabetic Retinopathy and Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2013;28:309-19, Chan-Hee Jung et al.)
- Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(1):103-104. Published online March 14, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.1.103
- 2,685 View
- 22 Download

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Association between Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy, Diabetic Retinopathy and Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Chan-Hee Jung, Ae-Rin Baek, Kyu-Jin Kim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Ji-Oh Mok
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(4):309-319. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.4.309
- 4,219 View
- 38 Download
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background It is not clear whether microangiopathies are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We investigated the relation of cardiac autonomic neuropathy (CAN) and other microangiopathies with carotid atherosclerosis in T2DM.
Methods A total of 131 patients with T2DM were stratified by mean carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) ≥ or <1.0 mm and the number of carotid plaques. CAN was assessed by the five standard cardiovascular reflex tests according to the Ewing's protocol. CAN was defined as the presence of at least two abnormal tests or an autonomic neuropathy points ≥2. Diabetic microangiopathies were assessed.
Results Patients with CAN comprised 77% of the group with mean CIMT ≥1.0 mm, while they were 29% of the group with CIMT <1.0 mm (
P =0.016). Patients with diabetic retinopathy (DR) comprised 68% of the group with CIMT ≥1.0 mm, while they were 28% of the group without CIMT thickening (P =0.003). Patients with CAN comprised 51% of the group with ≥2 carotid plaques, while they were 23% of the group with ≤1 carotid plaque (P =0.014). In multivariable adjusted logistic regression analysis, the patients who presented with CAN showed an odds ratio [OR] of 8.6 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6 to 44.8) for CIMT thickening and an OR of 2.9 (95% CI, 1.1 to 7.5) for carotid plaques. Furthermore, patients with DR were 3.8 times (95% CI, 1.4 to 10.2) more likely to have CIMT thickening.Conclusion These results suggest that CAN is associated with carotid atherosclerosis, represented as CIMT and plaques, independent of the traditional cardiovascular risk factors in T2DM. CAN or DR may be a determinant of subclinical atherosclerosis in T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carotid atherosclerosis: An independent risk factor for small fiber nerve dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Simin Guo, Yali Jing, Chenxi Li, Dalong Zhu, Weimin Wang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(2): 289. CrossRef - Evaluating Diagnostic Ultrasound of the Vagus Nerve as a Surrogate Marker for Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetic Patients
Bianka Heiling, Adriana Karl, Nadin Fedtke, Nicolle Müller, Christof Kloos, Alexander Grimm, Hubertus Axer
Medicina.2023; 59(3): 525. CrossRef - Albuminuria but not low eGFR is closely associated with atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: an observational study
Jun-Wei Wang, Jiang-Feng Ke, Zhi-Hui Zhang, Jun-Xi Lu, Lian-Xi Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Value of the Advanced Lipoprotein Profile and Glycated Proteins on Diabetic Retinopathy
Josep Julve, Joana Rossell, Eudald Correig, Marina Idalia Rojo-Lopez, Nuria Amigó, Marta Hernández, Alicia Traveset, Marc Carbonell, Nuria Alonso, Didac Mauricio, Esmeralda Castelblanco
Nutrients.2022; 14(19): 3932. CrossRef - The relationship between carotid disease and retinopathy in diabetes: a systematic review
Jocelyn J. Drinkwater, Timothy M. E. Davis, Wendy A. Davis
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Carotid Disease and Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Parameters in Type 2 Diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study Phase II
Jocelyn J. Drinkwater, Fred K. Chen, Alison M. Brooks, Brad T. Davis, Angus W. Turner, Timothy M.E. Davis, Wendy A. Davis
Diabetes Care.2020; 43(12): 3034. CrossRef - Diabetic foot – invalidating complication of diabetes mellitus
Oana Manuela Spălăţelu, Sergiu Chirila, Leonard Gurgas, Vasile Sârbu
Medic.ro.2019; 3(129): 40. CrossRef - Clinical factors associated with the recovery of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ji Eun Jun, Seung-Eun Lee, Min Sun Choi, Sung Woon Park, You-Cheol Hwang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of carotid intima-media thickness with exercise tolerance test in type 2 diabetic patients
Ali Momeni, Abdolmajid Taheri, Maryam Mansuri, Ali Bazdar, Morteza Sedehi, Masoud Amiri
IJC Heart & Vasculature.2018; 21: 74. CrossRef - Cardiac autonomic neuropathy may play a role in pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in type 1 diabetes mellitus
Sarka Mala, Veronika Potockova, Lucie Hoskovcova, Pavlina Pithova, Marek Brabec, Jaroslava Kulhankova, Radan Keil, Lucie Riedlbauchova, Jan Broz
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2017; 134: 139. CrossRef - Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index and Indices of Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Akihiko Ando, Michiaki Miyamoto, Kazuhiko Kotani, Kenta Okada, Shoichiro Nagasaka, Shun Ishibashi
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Cardiac Involvement in Peripheral Neuropathies
Ahmet Z. Burakgazi, Soufian AlMahameed
Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease.2016; 17(3): 120. CrossRef - The relationship between vitamin D status and cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chan-Hee Jung, Sang-Hee Jung, Kyu-Jin Kim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Ji-Oh Mok
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2015; 12(5): 342. CrossRef - Atorvastatin Treatment for Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Chinese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Na Fang, Wei Han, Dandan Gong, Zou Chen, Yu Fan
Medicine.2015; 94(44): e1920. CrossRef - Cardiovascular complications in patients with autonomic failure
Valeria Milazzo, Cristina Di Stefano, Alberto Milan, Agnese Ravera, Gabriele Sobrero, Luca Sabia, Franco Veglio, Simona Maule
Clinical Autonomic Research.2015; 25(3): 133. CrossRef - Association of heart rate with albuminuria in a general adult population: the 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
H. S. Choi, J. W. Hong, J. H. Lee, J. H. Noh, D. J. Kim
Internal Medicine Journal.2015; 45(4): 428. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes-associated carotid plaque burden is increased in patients with retinopathy compared to those without retinopathy
Núria Alonso, Alicia Traveset, Esther Rubinat, Emilio Ortega, Nuria Alcubierre, Jordi Sanahuja, Marta Hernández, Angels Betriu, Carmen Jurjo, Elvira Fernández, Didac Mauricio
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: Association between Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy, Diabetic Retinopathy and Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2013;28:309-19, Chan-Hee Jung et al.)
Hyun-Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(1): 101. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Clinical utility of serum beta-2-microglobulin as a predictor of diabetic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes without renal impairment
M.K. Kim, K.-J. Yun, H.J. Chun, E.-H. Jang, K.-D. Han, Y.-M. Park, K.-H. Baek, K.-H. Song, B.-Y. Cha, C.S. Park, H.-S. Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism.2014; 40(6): 459. CrossRef - Association between Brachial-Ankle pulse wave velocity and cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes
Nan Wu, Xiaoling Cai, Kuanping Ye, Yintao Li, Min He, Weiwei Zhao, Renming Hu
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Carotid atherosclerosis: An independent risk factor for small fiber nerve dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



